What is the infected blood scandal and will there be compensation?
Thousands were infected with HIV and hepatitis C, in the worst treatment disaster in NHS history.

More than 30,000 people in the UK were infected with HIV and hepatitis C after being given contaminated blood products in the 1970s and 1980s.
A public inquiry has described the scale of the scandal as “horrifying” and accused doctors, the government and NHS of repeatedly failing patients.
The government says a final compensation scheme is being set up, and that some victims will receive interim payments of £210,000 from the summer onwards.
Who was given infected blood and how many died?
Two main groups of NHS patients were affected by what has been called the biggest treatment disaster in the history of the NHS.
Firstly, haemophiliacs – and those with similar disorders – who have a rare genetic condition which means their blood does not clot properly.
People with haemophilia A have a shortage of a clotting agent called Factor VIII, while people with haemophilia B don’t have enough Factor IX.
In the 1970s, a new treatment using donated human blood plasma was developed to replace these clotting agents.
But whole batches were contaminated with deadly viruses.
After being given the infected treatments, about 1,250 people in the UK with bleeding disorders developed both HIV and hepatitis C, including 380 children.
This video can not be played
To play this video you need to enable JavaScript in your browser.
Around two-thirds later died of Aids-related illnesses. Some unintentionally gave HIV to their partners.
Another 2,400 to 5,000 people developed hepatitis C on its own, which can cause cirrhosis and liver cancer.
It is difficult to know the exact number of people infected with hepatitis C, partly because it can take decades for symptoms to appear.
A second group of patients were given contaminated blood transfusions after childbirth, surgery or other medical treatment between 1970 and 1991.
The inquiry estimates between 80 and 100 of these people were infected with HIV, and about 27,000 with hepatitis C.
In total, it’s thought about 2,900 people have died.
The Haemophilia Society believes 650 people infected with contaminated blood products, or their bereaved partners, have died since the inquiry was announced in 2017.
What has the infected blood inquiry said?
Announcing its findings, the inquiry said victims had been failed “not once, but repeatedly”, and that the risk of viral infections in blood products had been known since 1948.
Inquiry chairman Sir Brian Langstaff said there had been a lack of openness from the authorities and elements of “downright deception”, including the destruction of documents.
He said half-truths were also told, so people did not know about the risk of their treatment, the availability of alternatives, or even whether they were infected.
“This disaster was not an accident,” said Sir Brian. “The infections happened because those in authority – doctors, the blood services and successive governments – did not put patient safety first.”
-
too little was done to stop importing blood products from abroad, which used blood from high-risk donors such as prisoners and drug addicts
-
in the UK, blood donations were accepted from high-risk groups such as prisoners until 1986
-
blood products were not heat treated to eliminate HIV until the end of 1985, although the risks were known in 1982
-
there was too little testing to reduce the risk of hepatitis, from the 1970s onwards
Will infected blood scandal victims get compensation?
The total cost of compensation is expected to run into billions.
The government has published a document setting out the amounts that individuals can expect to get.
A person infected with HIV, for example, can expect to receive compensation of between £2.2m and £2.6m. These are average ranges rather than upper and lower limits.
Those with a chronic hepatitis C infection, defined as lasting more than six months, could expect to receive between £665,000 and £810,000.
Examples of compensation awards for the family members of those infected are also given.
The partner of someone infected with HIV who is still alive today, for example, should expect to receive around £110,000, while a child could get £55,000.
If their loved-one has died and they were financially dependent on them, annual payments are available.
Outlining the scheme, Cabinet Office Minister John Glen said payments – which the government expects to start before the end of the year – would be exempt from tax and would not affect benefits.
In cases where people who would be entitled to compensation have died, the money will go to their estate.
Before final compensation is delivered, he said interim payments of £210,000 will be made, starting from the summer.
The government has been criticised for waiting until after the publication of the final report to announce what compensation will be offered.
Bereaved families heckled the prime minister in July 2023 when he told inquiry that the government would act as “quickly as possible”.
In late 2022, following advice from the inquiry, the government made interim payments of £100,000 each to around 4,000 surviving victims and some bereaved partners.

Infected blood inquiry: Read more

How did the infected blood scandal happen?
In the 1970s, the UK was struggling to meet the demand for blood-clotting treatments, so imported supplies from the US.
But much of the blood was bought from high-risk donors such as prison inmates and drug-users.
Factor VIII was made by pooling plasma from tens of thousands of donors.
If just one was carrying a virus, the entire batch could be contaminated.
UK blood donations were not routinely screened for hepatitis C until 1991, 18 months after the virus was first identified.
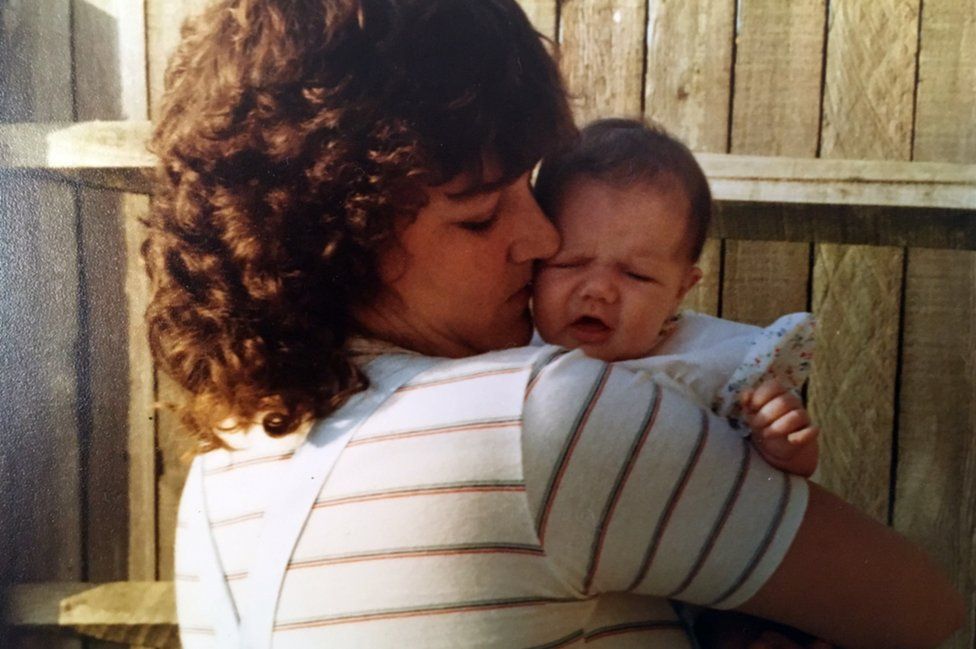

When did authorities know about infected blood?
By the mid-1970s, there were repeated warnings that imported US Factor VIII carried a greater risk of infection.
But attempts to make the UK more self-sufficient in blood products failed, so the NHS continued using foreign supplies.
Campaigners say haemophiliacs could have been offered an alternative treatment called Cryoprecipitate. This was much harder to administer, but was made from the blood plasma of a single donor, lowering the infection risk.
BBC News has also uncovered evidence children were infected with hepatitis C and HIV after being placed on clinical trials of new treatments – often, without their family’s consent.
As late as November 1983, the government insisted there was no “conclusive proof” that HIV could be transmitted in blood, a line robustly defended by former health minister Ken Clarke when he appeared before the inquiry.
This video can not be played
To play this video you need to enable JavaScript in your browser.
What happened in other countries affected by infected blood?
Many other countries were affected, although some – including Finland – used older treatments until much later rather than switch to Factor VIII, which minimised HIV infections.
Delivering the findings of the inquiry, Sir Brian Langstaff criticised UK government claims in the 1990s that screening for hepatitis C began as soon as the technology was available.
He said that 23 other countries – including Japan, Finland and Spain – introduced the screening before the UK.
In the US, companies that supplied infected products have paid out millions in out-of-court settlements.
Politicians and drug companies have been convicted of negligence in countries including France and Japan.
In his evidence to the inquiry, former health secretary Andy Burnham suggested there may be grounds for charges of corporate manslaughter in the UK.

Infected Blood: Time for Answers
Jim Reed meets the families of some of the children with bleeding disorders who were infected with HIV, to discuss their campaign for justice and what they hope for from the inquiry.